With the evolution of the internet and advancing digital marketing strategies, competitor mapping has now become an essential part of competitor research and analysis for all types and sizes of businesses.
Whether you’re launching a new product, entering a new market, or simply trying to stay ahead of the curve, competitor mapping provides the strategic insights you need to make informed decisions.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about competitor mapping, from basic concepts to advanced techniques that can transform how you approach competition analysis and strategic planning.
What is a competitive map?
A competitive map is a visual representation that plots your competitors based on specific criteria, helping you understand the competitive landscape at a glance. Think of it as a strategic GPS that shows you where your competitors stand in relation to your business and each other.
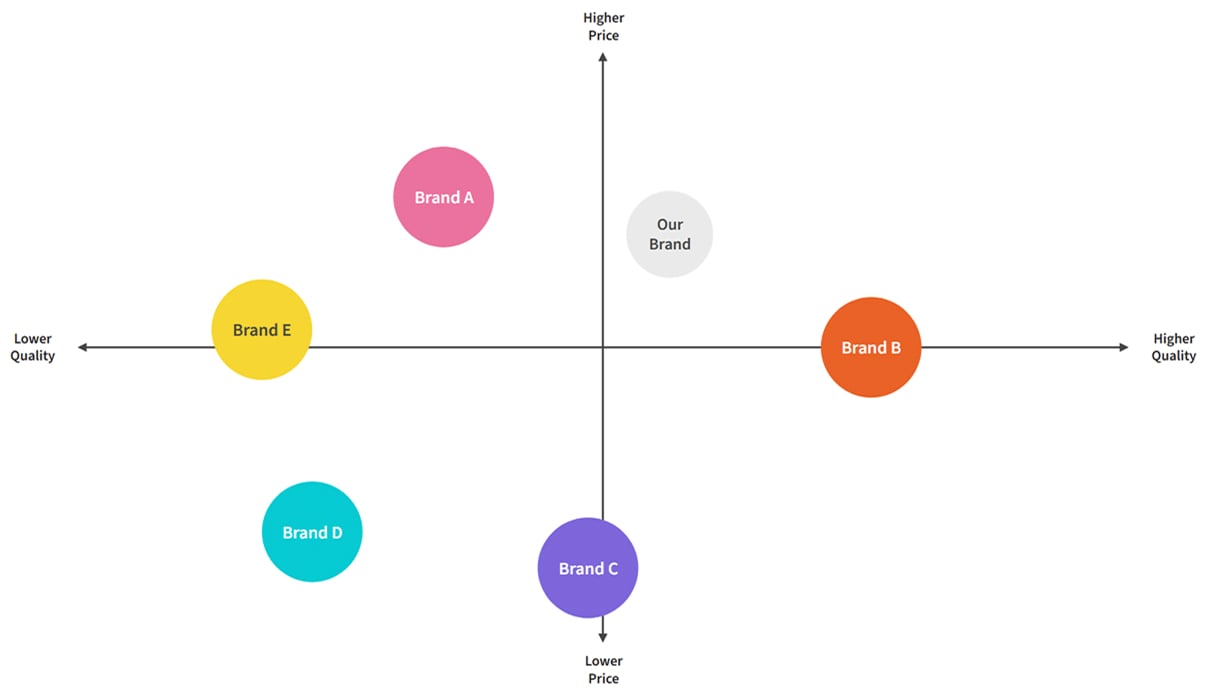
At its core, a competitive map serves as a strategic tool that identifies, categorizes, and analyzes competitors within your market space. It goes beyond simply listing who your competitors are. It also reveals their positioning, strengths, weaknesses, and strategic approaches.
The map typically displays competitors across two key dimensions, such as price versus quality, market share versus innovation, or customer satisfaction versus market presence. This visualization makes it easier to spot market gaps, identify opportunities for differentiation, and understand where your business fits within the broader competitive ecosystem.
Modern competitive intelligence tools have made creating these maps more sophisticated, allowing businesses to incorporate real-time data and multiple variables to create dynamic, actionable competitive landscapes.
Why competitor mapping matters
Understanding your competitors is vital to positioning your business strategically for long-term success. Competitor mapping provides the foundation for making informed strategic decisions that can significantly impact your market position.
Key benefits of competitor mapping
Competitor mapping delivers tangible value across multiple business functions, from product development to marketing strategy.
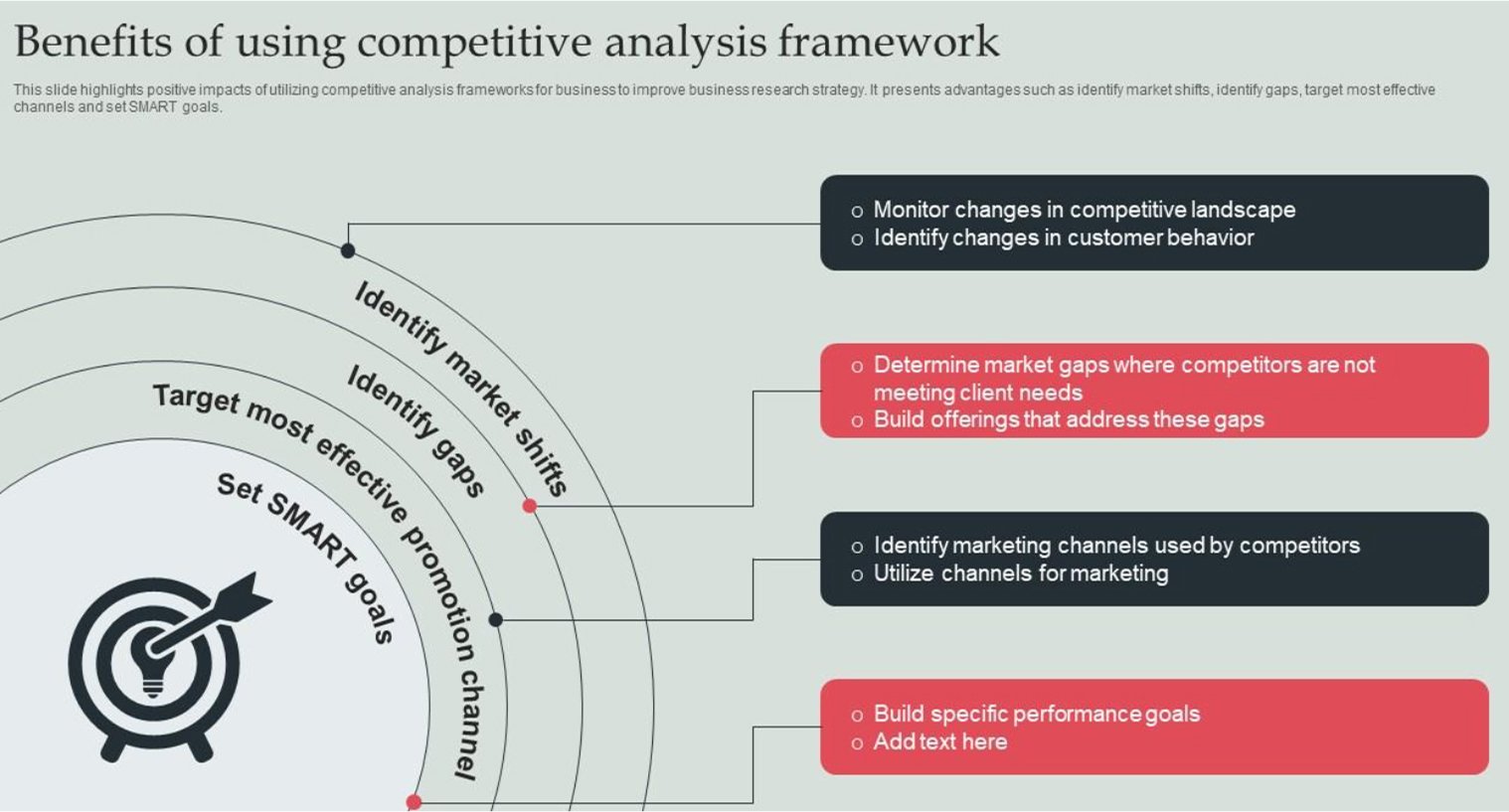
Understanding these benefits helps justify the investment in competitive intelligence and ensures you maximize the strategic value of your mapping efforts.
Identifying market gaps and opportunities
One of the most powerful aspects of competitor mapping is its ability to reveal untapped opportunities in your market. By plotting competitors across various dimensions, you can quickly identify areas where customer needs aren’t being fully met.
For instance, if your map shows that most competitors focus on either low-cost or premium offerings, you might discover a profitable middle-market opportunity. These gaps represent potential blue ocean strategies where you can create uncontested market space.
Improving product development
Competitor mapping directly informs product development by showing you what features, services, or capabilities are missing from the current market offerings. This insight helps you prioritize development resources and create products that truly differentiate your business.
When you understand where competitors are investing their resources and where they’re falling short, you can make strategic decisions about feature development, user experience improvements, and innovative solutions that set you apart.
Optimizing pricing and positioning strategies
Your competitive map reveals pricing patterns and positioning strategies across your market, enabling you to make informed decisions about your own pricing structure. You can identify whether you should compete on price, premium value, or unique positioning.
This analysis is particularly valuable for social media marketing agencies looking to position their services competitively while maintaining healthy profit margins.
Enhancing marketing effectiveness
Understanding how competitors message their value propositions, target their audiences, and execute their marketing campaigns enables you to refine your own marketing approach.
You can identify messaging gaps, discover underserved audience segments, and develop marketing strategies that cut through the competitive noise more effectively.
Using competitor mapping for strategic decisions
Competitor mapping provides the data foundation for major strategic decisions, from market entry strategies to expansion plans. It helps you assess market saturation, identify potential acquisition targets, and evaluate the competitive intensity of different market segments.
Types of competitors to identify
Not all competitors are created equal, and effective competitor mapping requires understanding the different types of competitive threats you face. Each type requires different analysis approaches and strategic responses.
Direct competitors
Direct competitors offer similar products or services to the same target market. These are your most obvious competitors and the ones customers actively compare you against when making purchasing decisions.
For example, if you run a social media management agency, other agencies offering similar services like social media management, content creation, and analytics reporting would be your direct competitors.
Direct competitors typically:
- Target the same customer segments
- Offer similar solutions to the same problems
- Compete directly for the same market share
- Use similar distribution channels and pricing models
Indirect competitors
Indirect competitors solve the same customer problem but through different methods or approaches. These competitors might not be obvious at first glance, but they’re often the most disruptive to your business model.
Consider how Netflix wasn’t initially seen as a direct competitor to traditional cable TV, but ultimately transformed the entire entertainment industry. Similarly, AI tools for social media might compete indirectly with traditional marketing agencies by offering automated solutions.
Indirect competitors often:
- Address the same customer pain points with different solutions
- May have different business models or pricing structures
- Could evolve into direct competitors over time
- Often bring innovative approaches that disrupt established markets
Emerging competitors
Emerging competitors represent future threats and opportunities. These might be startups, companies expanding from adjacent markets, or established players developing new competitive solutions.
Identifying emerging competitors early gives you a strategic advantage. You can monitor their progress, learn from their innovations, and potentially adapt their successful strategies before they become major threats.
Keep an eye on:
- Well-funded startups in your space
- Adjacent market players expanding their offerings
- Technology developments that could create new competitive solutions
- Changing customer behaviors that might favor new types of solutions
How to do competitor mapping step by step?
Creating an effective competitive map requires a systematic approach that ensures you capture accurate, actionable insights.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step process to guide your competitor mapping efforts.
Step 1: Setting objectives and choosing focus areas
Before diving into data collection, clearly define what you want to achieve with your competitor mapping exercise. Your objectives will determine which competitors to include, what data to collect, and how to structure your analysis.

Common objectives include:
- Understanding market positioning opportunities
- Identifying pricing optimization strategies
- Discovering product development gaps
- Analyzing marketing message differentiation
- Assessing competitive threats and opportunities
Once you’ve established objectives, choose 2-3 focus areas that will form the axes of your competitive map. These might include:
- Price vs. quality
- Market share vs. innovation
- Features vs. ease of use
- Geographic reach vs. specialization
- Customer satisfaction vs. market presence
Step 2: Data collection methods and sources
Effective competitor mapping relies on comprehensive, accurate data. Develop a systematic approach to gathering information from multiple sources to ensure you get a complete picture of your competitors:
Primary research methods:
- Customer interviews and surveys
- Mystery shopping or service testing
- Industry conferences and networking events
- Direct competitor website analysis
- Social media monitoring and sentiment tracking
Secondary research sources:
- Industry reports and market research
- Financial filings and earnings calls
- Press releases and news coverage
- Patent filings and product announcements
- Professional networking platforms like LinkedIn
Digital intelligence tools:
- Website traffic and SEO analysis tools
- Social media analytics platforms
- Review site monitoring
- Pricing intelligence software
- Competitor analysis tools
Step 3: Analyzing competitor positioning and strategies
Once you’ve collected data, analyze each competitor’s strategic positioning. Look beyond surface-level information to understand their underlying business strategies, target markets, and value propositions.
Key analysis areas include:
- Target customer segments and personas
- Value proposition and messaging strategies
- Product or service differentiation points
- Pricing strategies and business models
- Marketing channels and tactics
- Operational strengths and weaknesses
For example, social media marketing can analyze competitors’ content strategies, engagement rates, platform preferences, and client portfolio positioning.
Step 4: Visualizing your competitive landscape
Transform your analysis into visual competitive maps that make insights immediately actionable. Create multiple maps focusing on different strategic dimensions to provide comprehensive competitive intelligence.
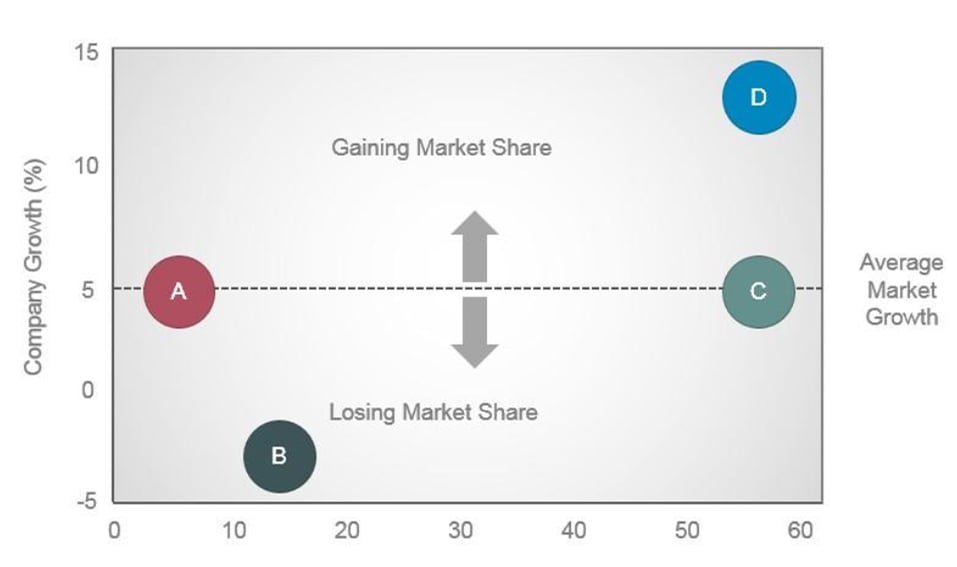
Design your maps to be:
- Easy to understand at a glance
- Regularly updatable as conditions change
- Shareable across your organization
- Actionable for strategic decision-making
Include your own business on the map to see how you compare and identify positioning opportunities or threats that require strategic attention.
Essential components of effective competitor mapping
A comprehensive competitor mapping exercise includes several key components that work together to provide strategic insights. Each component contributes a unique value to your competitive intelligence efforts.
Competitor profiling
Detailed competitor profiles form the foundation of effective mapping. Each profile should capture both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights about your competitors’ strategies and market approach.
Key profile elements:
- Company background and history
- Leadership team and key personnel
- Financial performance and funding
- Product/service portfolio analysis
- Target market and customer base
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Technology stack and operational approach
- Recent strategic moves and announcements
These profiles should be living documents that you update regularly as competitors evolve their strategies or market conditions change.
SWOT analysis
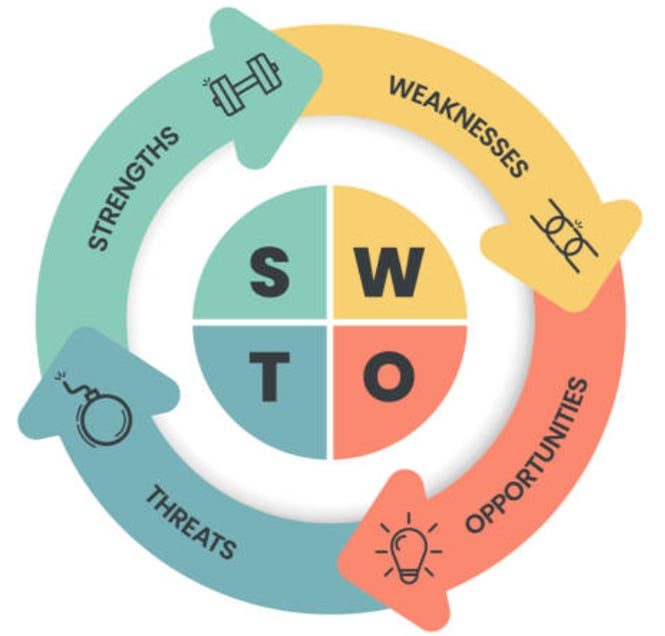
Conduct a thorough SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for each major competitor. This framework helps you understand not just what competitors do, but how effectively they execute their strategies.
Strengths analysis:
- Market-leading capabilities or features
- Strong brand recognition or customer loyalty
- Operational efficiencies or cost advantages
- Strategic partnerships or distribution channels
Weaknesses identification:
- Service gaps or quality issues
- Limited market presence or customer segments
- Operational constraints or resource limitations
- Negative customer feedback or reputation issues
Opportunities assessment:
- Market segments they’re not serving
- Geographic expansion possibilities
- Product development opportunities
- Partnership or acquisition potential
Threats evaluation:
- Competitive vulnerabilities you could exploit
- Market trends that might disadvantage them
- Regulatory or technology changes
- Customer behavior shifts
Business model comparative analysis
Understanding how competitors structure their business models, such as B2C or B2B, provides insights into their strategic priorities, revenue sources, and operational constraints. This analysis helps you identify alternative approaches and potential disruption opportunities.
Compare elements such as:
- Revenue models (subscription, transaction-based, advertising, etc.)
- Cost structures and operational approaches
- Customer acquisition and retention strategies
- Partnership and distribution models
- Technology and platform strategies
For agencies using social media management tools, this might involve comparing how different platforms structure their pricing, feature sets, and client service models.
Market positioning assessment
Analyze how competitors position themselves in the market and communicate their value to customers. This assessment reveals messaging opportunities and helps you understand how customers perceive different competitive options.
Key positioning elements include:
- Brand messaging and value propositions
- Target audience definition and communication
- Pricing strategy and positioning
- Feature emphasis and differentiation
- Market leadership claims and proof points
Competitor mapping tools and techniques
The right tools can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your competitor mapping efforts. From free resources to sophisticated intelligence platforms, choose tools that match your business objectives and budget.
Free competitor analysis tools and resources
Many powerful competitor analysis capabilities are available at no cost, making them excellent starting points for small businesses or those new to competitive intelligence.
Website and SEO analysis
- Google Analytics (for your own performance comparison)
- Ahrefs free tools (backlink and keyword analysis)
- SimilarWeb (website traffic estimates)
Social media monitoring:
- Google Alerts (mention tracking)
- Social media platform native analytics
- ContentStudio’s free tools (social media competitor analytics)
General research tools:
- Google Trends (search interest analysis)
- LinkedIn Sales Navigator free trial (company intelligence)
- Glassdoor (employee insights and company culture)
- Crunchbase free tier (startup and funding information)
Professional competitive intelligence software
Professional tools provide advanced capabilities for comprehensive competitor mapping, automated data collection, and sophisticated analysis features.
Enterprise intelligence platforms:
- Crayon (competitive intelligence automation)
- Klenty (sales intelligence and outreach)
- Kompyte (real-time competitive monitoring)
- SimilarTech (technology stack analysis)
Market research platforms:
- CB Insights (market intelligence and trends)
- PitchBook (private market data)
- IBISWorld (industry analysis and benchmarking)
- Forrester and Gartner research reports
Social media monitoring and sentiment analysis tools
Social media provides real-time insights into competitor performance, customer sentiment, and market positioning. Analytics tools designed for social media can automate much of this monitoring and analysis.
Platform-specific tools:
- Facebook business manager (competitor page analysis)
- Twitter/X analytics (engagement and reach comparison)
- LinkedIn company pages insights
- Instagram business insights
- ContentStudio.io (multi-platform social media management and analytics)
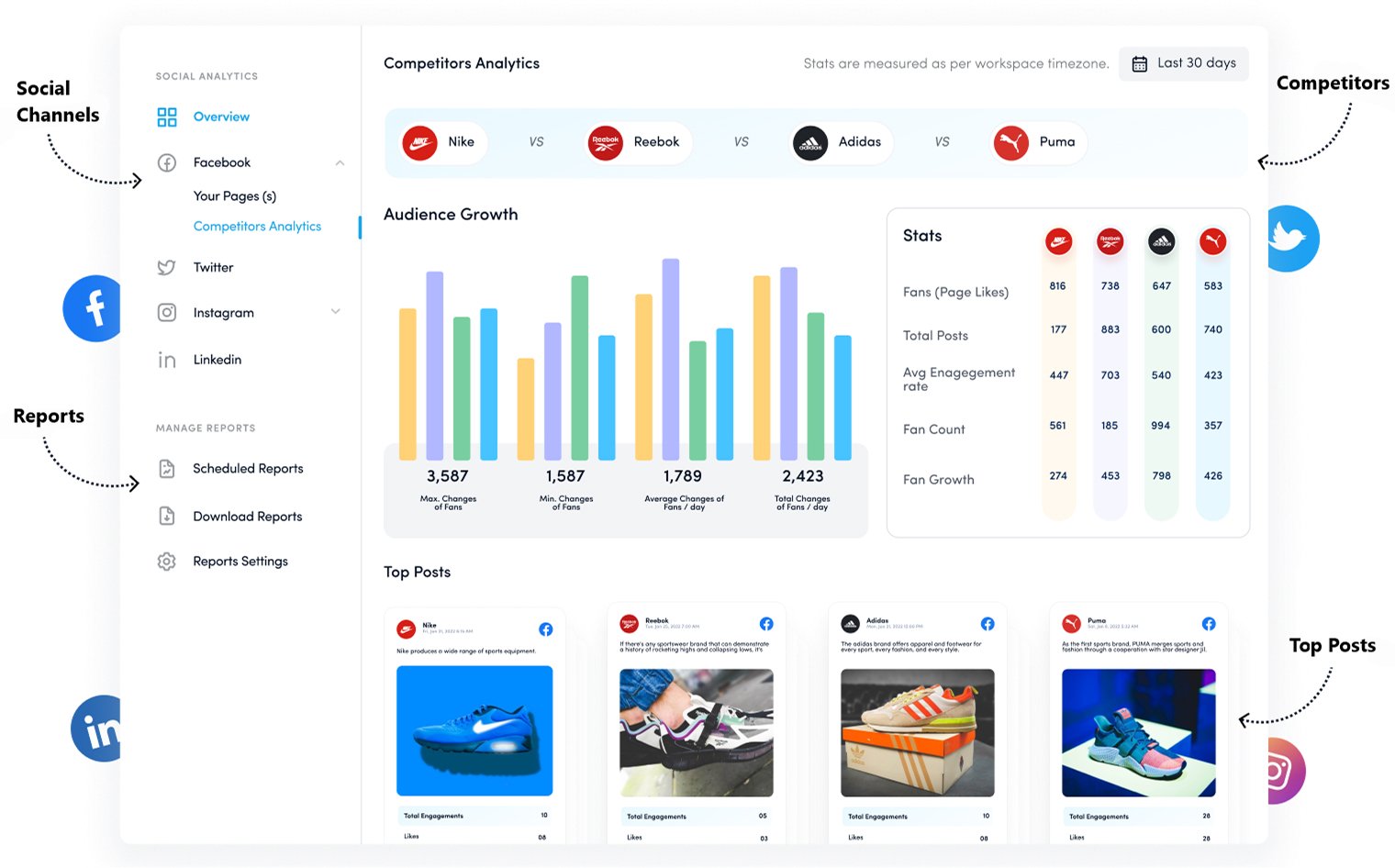
These tools can help you track competitor social media engagement, content performance, audience growth, and customer sentiment in real time.
Social Media Analytics
Fine-tune your social media strategy for success with in-depth analytics and white-labeled reports.
Get Started for FREE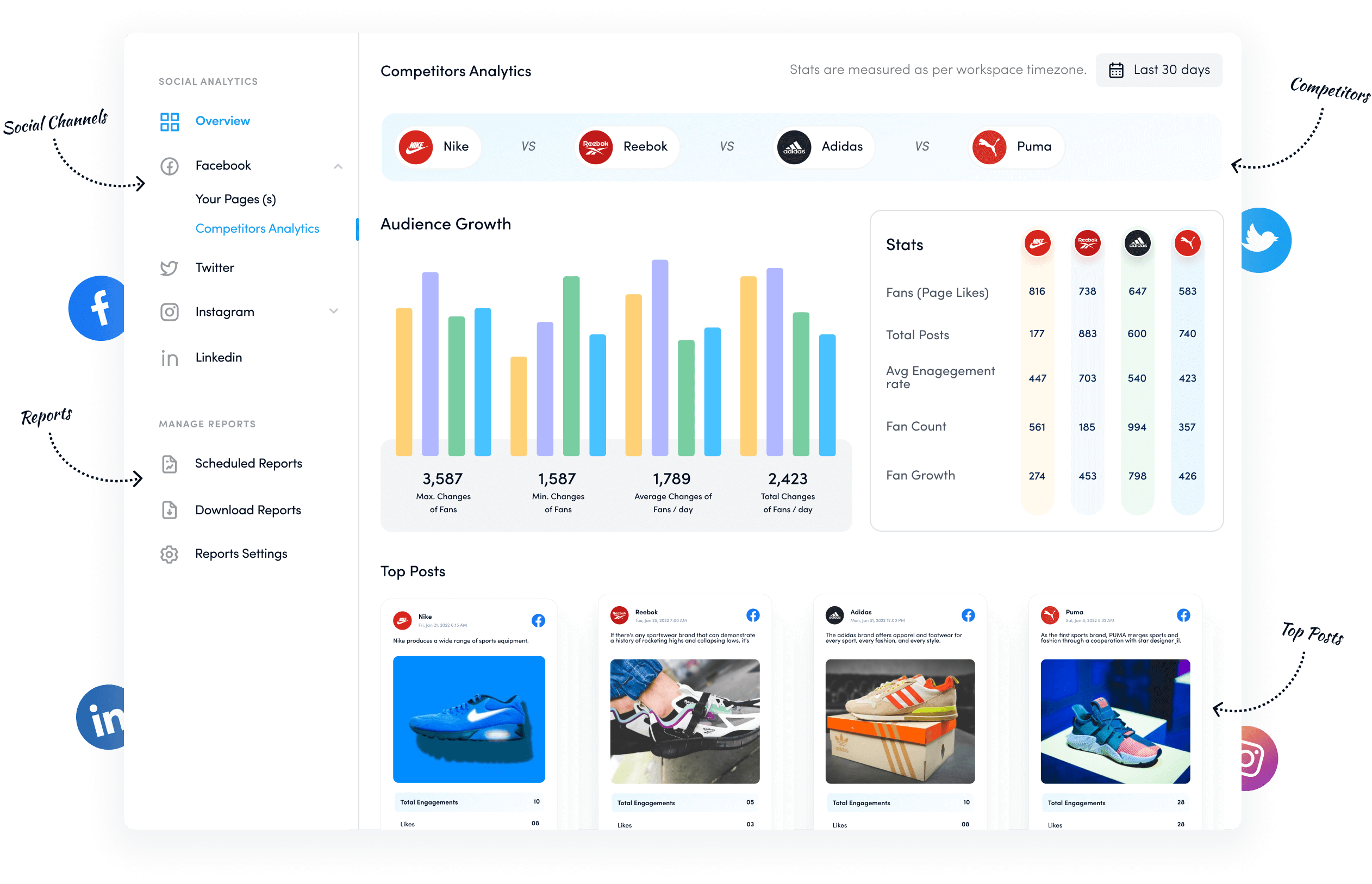
Real-world competitor mapping examples
Understanding competitor mapping concepts is one thing but seeing them applied in real-world scenarios helps clarify how to create actionable competitive intelligence.
Here are innovative examples from companies that used competitor mapping to gain significant strategic advantages.
Example 1: Netflix vs Disney+ streaming wars
The streaming industry provides one of the most compelling examples of real-time competitor mapping in action. When Disney+ launched in 2019, Netflix made a promise to release an original movie every week of 2021 in response to the competitive threat.
Disney’s competitive mapping revealed a strategic opportunity in the pricing dimension. Disney+ had an innovative pricing structure during its first two years post-launch.
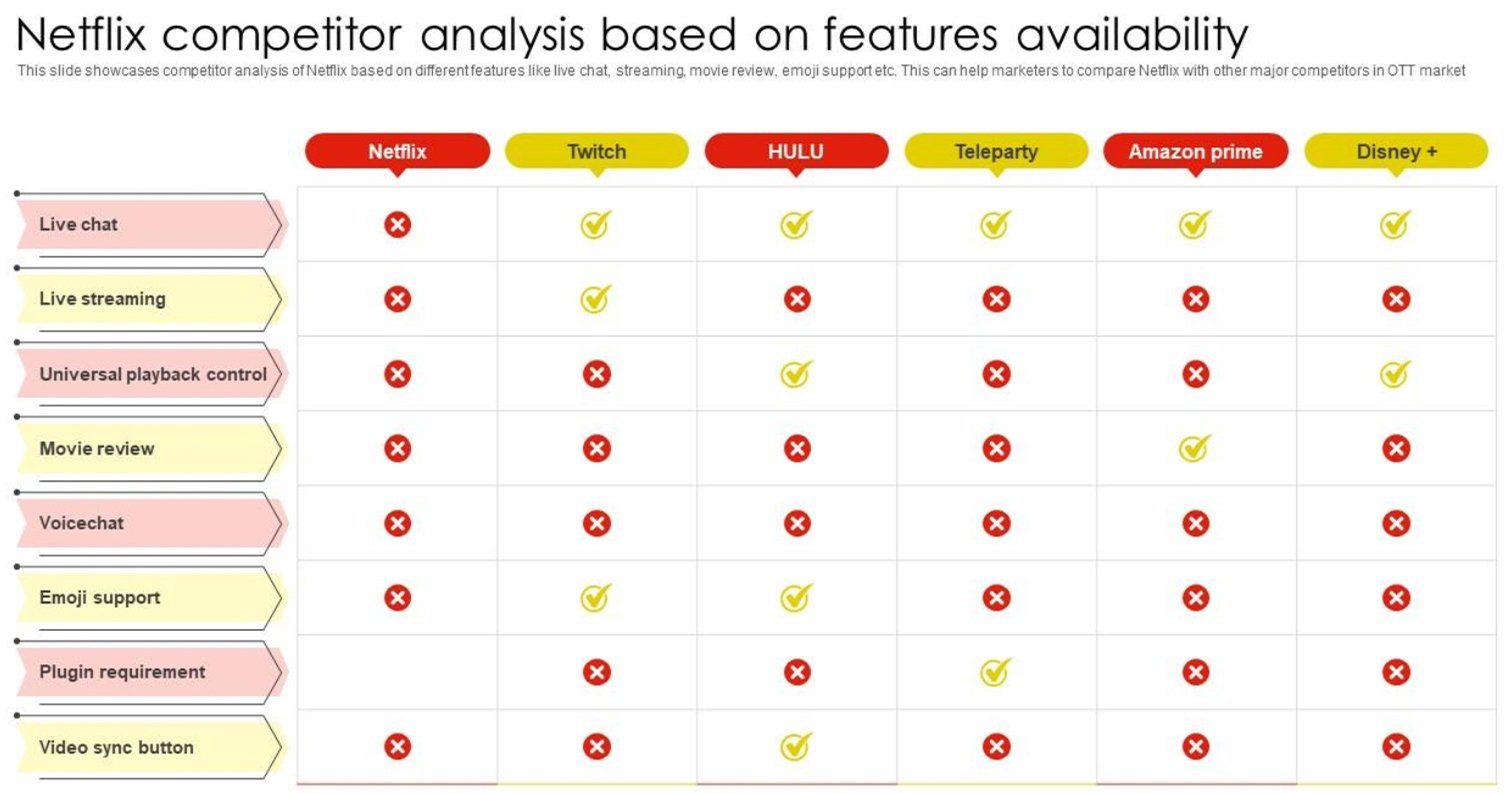
The competitive map revealed different strategic positions:
- Content breadth vs. pricing: Netflix positioned itself with diverse, global content at premium pricing
- Brand loyalty vs. market penetration: Disney leveraged exclusive franchises (Marvel, Star Wars, Pixar) for rapid subscriber acquisition
- Global reach vs. family focus: Netflix’s worldwide presence versus Disney’s family-friendly positioning
This mapping enabled both companies to identify their competitive advantages and develop targeted strategies for market differentiation.
Example 2: Motorola’s iPhone response
The classic case of Motorola’s Razr2 response to Apple’s iPhone launch demonstrates how the competitor mapping process can reveal market disruption in real time. In 2007, eight weeks separated the launch of Apple’s revolutionary iPhone and Motorola’s next-generation Razr2 cellular telephone.
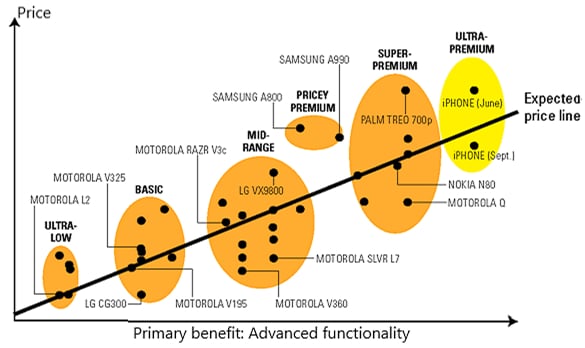
Motorola used competitive positioning maps to assess whether the iPhone would compete directly with the Razr2 or create an entirely new market segment. The analysis revealed that while Motorola had products in four of five market clusters, they had no presence in the ultrapremium segment that the iPhone was pioneering.
Most importantly, the mapping showed that traditional advantages like battery life and call clarity had become hygiene factors rather than differentiators. This insight revealed that Motorola’s core competitive advantages were no longer sufficient for market differentiation.
Example 3: Amazon’s real-time competitive pricing
Amazon’s competitor mapping process operates at a massive scale, analyzing millions of products in terms of price competitiveness and demand velocity. Their system continuously monitors competitor pricing and automatically adjusts prices to maintain market position.
The innovation lies in their predictive competition mapping, meaning Amazon doesn’t just react to competitor price changes; they anticipate them. Their system maps seasonal patterns, competitor inventory levels, and market demand to predict when competitors will change prices, often adjusting their own prices proactively.
These examples show how innovative companies use competitor mapping not just for analysis but as the foundation for automated, strategic decision-making systems that provide sustainable competitive advantages.
Best practices for competitor mapping
Effective competition mapping requires ongoing commitment and systematic approaches to ensure your competitive intelligence remains accurate and actionable over time. Some of the key best practices for the competitor mapping process are:
Maintaining accurate and current data
Competitive landscapes change rapidly, making data freshness critical for effective decision-making. Outdated competitive intelligence can lead to poor strategic choices and missed opportunities.
- Schedule monthly updates for key metrics and quarterly comprehensive reviews
- Cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy
- Use automation tools like Google Alerts and social media monitoring for real-time insights
Building a competitive intelligence system
Transform ad hoc competitor analysis into a systematic competitive intelligence capability that supports ongoing strategic decision-making.
- Designate competitive intelligence champions and define clear responsibilities
- Create centralized competitor databases with cross-functional access
- Establish reporting schedules and escalation processes for significant threats
Collaborating across teams for comprehensive insights
An effective competitor mapping process benefits from diverse perspectives across your organization. Different teams interact with competitors in various ways, providing unique insights.
- Sales teams provide direct competitor encounters, pricing insights, and win/loss analysis
- Marketing teams offer content analysis, social media comparisons, and brand positioning insights
- Product teams contribute feature comparisons, user experience trends, and development priorities
Updating and maintaining competitor profiles
Static competitor profiles quickly become outdated and lose strategic value. Implement systematic processes to keep competitive intelligence current and actionable.
- Schedule quarterly comprehensive updates and track significant changes immediately
- Add new data sources and expand analysis depth for key strategic competitors
- Remove or de-prioritize competitors who are no longer relevant to your market
Turning insights into actionable strategies
The ultimate goal of competitor mapping is strategic action. Bridge the gap between competitive intelligence and strategic implementation through clear action planning.
- Translate competitive insights into specific opportunities with assigned ownership and timelines
- Monitor competitor responses to your strategic moves and adjust accordingly
- Document lessons learned and continuously refine your competitive strategy based on results
This systematic approach to competition mapping ensures that your competitive intelligence efforts translate into sustainable competitive advantages and improved market positioning.
Conclusion
Competitor mapping is about understanding the strategic landscape and positioning your business for success. Through systematic analysis and ongoing monitoring, you can identify opportunities and make informed decisions that drive growth.
The key is treating it as an ongoing process, not a one-time analysis. Collect data, analyze strategically, and act decisively on your findings today to uncover the strategic advantages waiting in your competitive landscape.
FAQs
What is competition mapping?
Competition mapping is the process of identifying and analyzing competitors within your market. It involves collecting data about competitors’ strategies, strengths, and weaknesses, then organizing this information into visual maps to understand the competitive landscape and identify strategic opportunities.
What are the 4 P’s of competitor analysis?
The 4 P’s of competitor analysis are Product (competitors’ features, quality, and offerings), Price (pricing strategies and value positioning), Place (distribution channels and market coverage), and Promotion (marketing strategies and brand messaging). This framework ensures comprehensive analysis of major competitive factors that influence market success.
What is an example of competitor mapping?
A social media management company could map competitors using “pricing” and “feature comprehensiveness” as axes. This might reveal budget tools and enterprise platforms while identifying gaps such as affordable comprehensive solutions. This visualization helps spot positioning opportunities and guides strategic decisions to capture underserved market segments.
